anabolism and catabolism
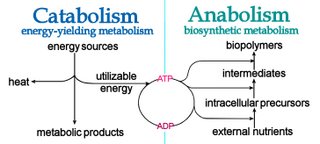 Anabolism, as in ‘anabolic steroids’, refers to those metabolic processes that utilize energy to biosynthesize complex molecules and to generate growth.
Anabolism, as in ‘anabolic steroids’, refers to those metabolic processes that utilize energy to biosynthesize complex molecules and to generate growth.The reverse process is catabolism, whereby nutrients are broken down to release energy. Catabolic processes provide intermediates for synthetic or further catabolic pathways and release energy, usually as the energy carrier molecules ATP and NADPH.
The following mnemonic may help in remembering the difference: "A B C D" : Anabolism = Biosynthesis ; Catabolism = Degradation
anabolic pathways : for a complete list see topics or sidebar • acetyl CoA pathway • Calvin cycle • C-3 • C-4 • CAM • HMG-CoA-reductase pathway • Isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants methylerythritol phosphate & HMG-CoA-reductase pathway • Light-reactions • MVA independent • Nonoxygenic photosynthesis • Oxygenic photosynthesis • Photosynthesis Overview • Photophosphorylation •
catabolic pathways: for a complete list see topics or sidebar • anaplerotic reactions • beta-oxidation • glycolysis • glyoxylate cycle • Krebs cycle • oxidative phosporylation •
Labels: anabolism, catabolism, mnemonic






































0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home